[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] The earth ionosphere refers to the area where the neutral atmosphere is partially ionized at an altitude of 60 to 1000 km. At the low latitude equator, the dynamics of the ionospheric plasma are affected by the polarity change of the interplanetary magnetic field Bz. The interplanetary penetration electric field caused by it can lead to the redistribution of the ionospheric plasma at low latitudes, resulting in the spatiotemporal change of the ionosphere.
Total ionospheric electron concentration (TEC) is an important parameter for describing the ionosphere. Ionospheric TEC based on GPS beacon observation inversion has been widely used in the study of large-scale changes in the ionosphere. However, because the position of the ionospheric penetration point is constantly changing due to GPS satellite movement, the time series of observations also contains information about changes in space and time, and it is difficult to obtain detailed changes in ionosphere TEC with space and time using GPS observations.
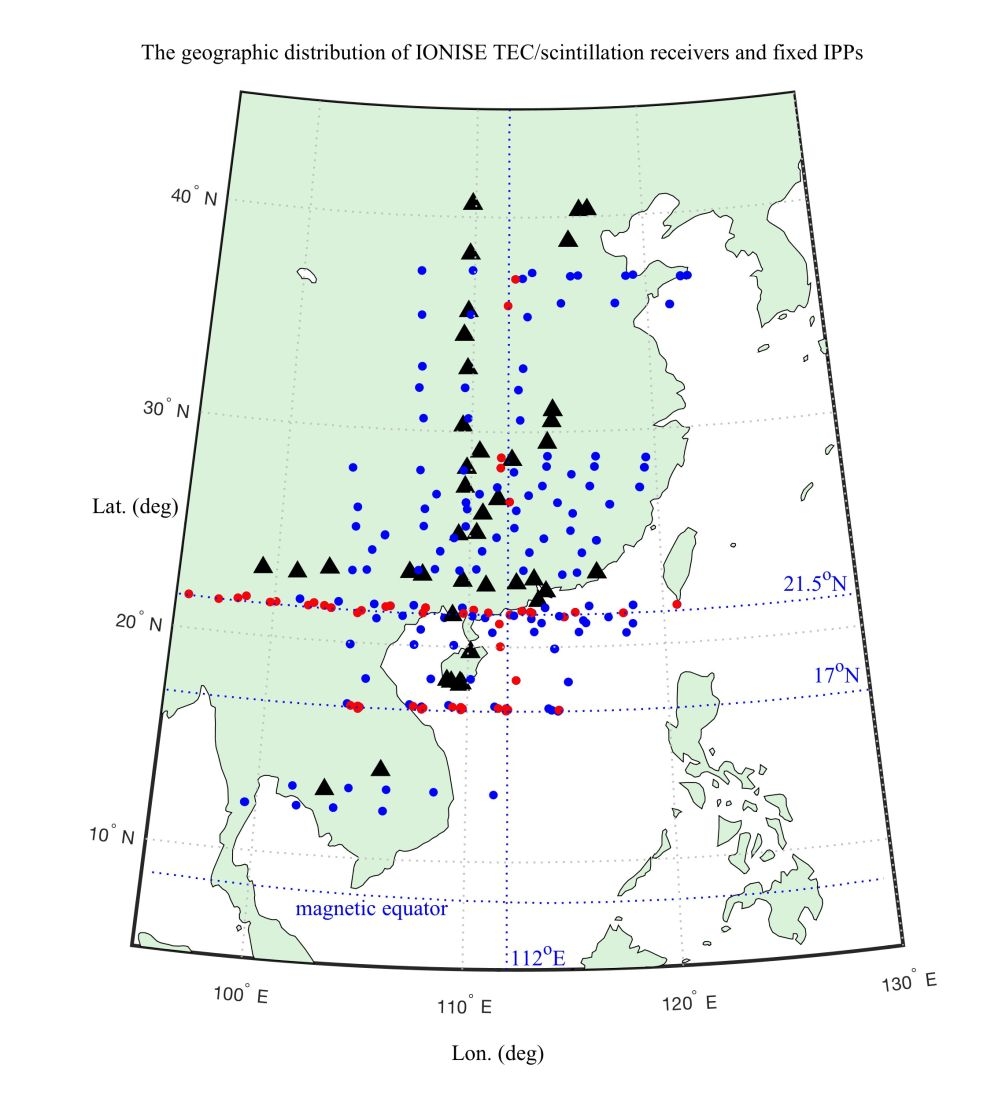
In recent years, China has launched a series of Beidou satellites for global networking. The Beidou satellite navigation system includes multiple geosynchronous orbit satellites, and the position of the ionospheric penetration point is almost unchanged, which provides the possibility to study the fine-temporal variation of the ionospheric TEC. In recent years, the Beijing National Institute of Space Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences has three research directions around South China and its surrounding areas-ionosphere heterogeneous body / scintillation generation and tracking, ionospheric disturbance and excitation source and ionosphere Regional characteristics of fine structure, dedicated to the construction of East Asia / Southeast Asia ionospheric heterogeneous body / scintillation observation network (IONISE, http://ionise.geophys.ac.cn/). At present, Beijing National Space Environment National Station has developed a multi-satellite beacon TEC / scintillation automatic observation system. A “cross†observation chain has been established along 110 degrees east longitude and 23 degrees north latitude, and a multi-base portable ionization has been established in Hainan and South Island Reefs in China. Layer Detector PDI. These make IONISE a large-scale, dense ionospheric fixed penetration point TEC detection capability (Figure 1) and rapid detection of ionospheric motion, which can obtain the fine-temporal changes in the ionosphere in southern China and surrounding areas.
On April 20, 2018, a moderate intensity magnetic storm occurred (SYM-H reached -86 nT), and the polarity of the interplanetary magnetic field Bz showed periodic changes. Li Guozhu, a researcher of the Institute of Geology and Earth, and other researchers used the IONISE Beidou synchronous satellite TEC and PDI fast Doppler detection to find that the low-latitude ionosphere TEC has a periodic enhancement phenomenon in a large longitude range (Figure 2). They combined PDI Doppler, geomagnetic ΔH, and interplanetary magnetic field Bz data for analysis, and found that the periodic enhancement of the low-latitude ionosphere TEC is closely related to the periodic downward drift of the plasma (Figure 3): at the interplanetary magnetic field Bz pole During the multiple changes in the nature, multiple interplanetary westward penetrating electric fields drove the low-latitude ionospheric plasma in a wide range of longitude regions downward, causing the density of the ionosphere top to drop, and the ionospheric plasma at the high latitude top to low. Latitude motion fills this low-density region, causing an increase in the low-latitude ionosphere TEC. During magnetic storms, the increase in low-latitude ionosphere TEC observed in the past is generally explained by the interplanetary eastward penetrating electric field lifting the ionosphere, which is caused by the upward movement of the plasma. Their observations show another possible process of the magnetosphere-low-latitude ionosphere coupling affecting the ionospheric structure.
The research results are published in the international journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Micro Pins Material is stainless steel,carbon steel and brass,it is available in .017 (.43) to .080 (2.03) diameters
Space saving design for high density packaging Ideal for mating with our standard line of micro jacks
Available for press-fit, swage or solder mounting
Micro Pins used wildly in Electronic .
Micro Pins
Micro Pins,Micro Spring Pins,Electric Micro Pins,Stainless Steel Micro Pins
Shenzhen Long Wei Wang Precision Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.electronichdwe.com
